
Light Sport Aviation Training
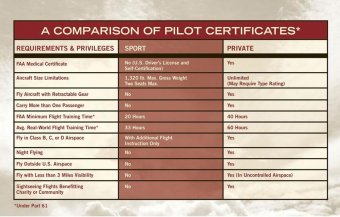
Training Requirements
- Meet the minimum age requirement:
- Be at least 16 to become a student pilot and fly solo (14 for gliders).
- Be at least 17 to test for a sport pilot certificate (16 for gliders).
- Be able to read, write, and understand English.
- Hold a current and valid U.S. driver’s license as evidence of medical eligibility (provided the FAA did not deny, revoke, or suspend your last medical certificate application). Alternatively, you can also use a third class airman’s medical to establish medical fitness.
- Pass an FAA sport pilot knowledge test, also known as the written test.
- Complete a minimum of 20 hours of training for an airplane; times vary for other aircraft types.
- Pass an FAA sport pilot practical test, also known as the flight test or checkride.
Privileges
The holder of a valid sport pilot certificate may:
- Operate as pilot in command of a sport pilot eligible aircraft (Cessna 162 Skycatcher).
- Carry a single passenger and share expenses (fuel, oil, airport expenses, and aircraft rental).
- Fly during the daytime using visual flight rules (VFR). Three statute miles visibility and visual contact with the ground are required.
- Fly Cross-country anywhere in the U.S.
- Fly up to 10, 000 feet above mean sea level (MSL) or 2, 000 feet above ground level (AGL), whichever is higher.
- Fly in Class E and G airspace (and B, C, and D airspace with appropriate training).
Limitations
Sport pilots may not:
- Fly in Class A airspace.
- Fly in Class B, C, or D airspace until they receive training and a logbook endorsement from an instructor.
- Fly outside the U.S. without prior permission from the foreign aviation authority.
- Tow any object.
- Fly while carrying a passenger or property for compensation or hire.
Source: www.flyftm.com









